Computer Operating Properly on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A watchdog timer (WDT, or simply a ''watchdog''), sometimes called a ''computer operating properly timer'' (''COP timer''), is an electronic or software
A watchdog timer (WDT, or simply a ''watchdog''), sometimes called a ''computer operating properly timer'' (''COP timer''), is an electronic or software
 Watchdog timers are commonly found in
Watchdog timers are commonly found in
 The act of restarting a watchdog timer is commonly referred to as ''kicking'' the watchdog. In electronic watchdogs, kicking is typically done by writing to a watchdog control
The act of restarting a watchdog timer is commonly referred to as ''kicking'' the watchdog. In electronic watchdogs, kicking is typically done by writing to a watchdog control
File:Watchdog timer state diagram with autostart.svg, Unconditionally enabled watchdog
File:Watchdog timer state diagram with enable.svg, Watchdog with ''enable'' input signal
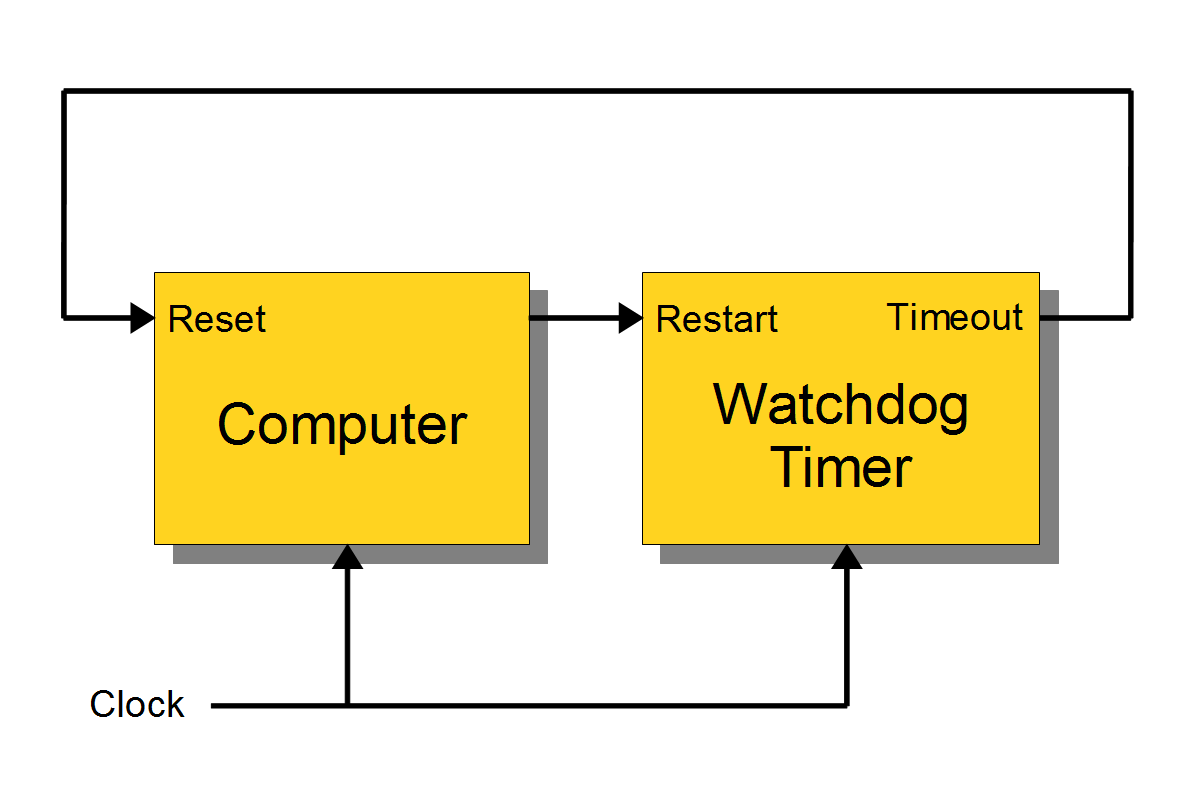
When automatically generated, the enabling signal is typically derived from the computer reset signal. In some systems the reset signal is directly used to enable the watchdog. In others, the reset signal is delayed so that the watchdog will become enabled at some later time following the reset. This delay allows time for the computer to boot before the watchdog is enabled. Without this delay, the watchdog would timeout and invoke a subsequent reset before the computer can run its application software — the software which kicks the watchdog — and the system would become stuck in an endless cycle of incomplete reboots.

 For example, the above diagram shows a likely configuration for a two-stage watchdog timer. During normal operation the computer regularly kicks Stage1 to prevent a timeout. If the computer fails to kick Stage1 (e.g., due to a hardware fault or programming error), Stage1 will eventually timeout. This event will start the Stage2 timer and, simultaneously, notify the computer (by means of a non-maskable interrupt) that a reset is imminent. Until Stage2 times out, the computer may attempt to record state information, debug information, or both. As a last resort, the computer will be reset upon Stage2 timeout.
For example, the above diagram shows a likely configuration for a two-stage watchdog timer. During normal operation the computer regularly kicks Stage1 to prevent a timeout. If the computer fails to kick Stage1 (e.g., due to a hardware fault or programming error), Stage1 will eventually timeout. This event will start the Stage2 timer and, simultaneously, notify the computer (by means of a non-maskable interrupt) that a reset is imminent. Until Stage2 times out, the computer may attempt to record state information, debug information, or both. As a last resort, the computer will be reset upon Stage2 timeout.
 In computers that are running an operating system and multiple processes, a single, simple test might be insufficient to guarantee normal operation, as it could fail to detect a subtle fault condition and consequently kick the watchdog even though a fault condition exists. For example, in the case of the Linux operating system, a user-space watchdog
In computers that are running an operating system and multiple processes, a single, simple test might be insufficient to guarantee normal operation, as it could fail to detect a subtle fault condition and consequently kick the watchdog even though a fault condition exists. For example, in the case of the Linux operating system, a user-space watchdog
entity watchdog_timer is
port (
CLK : in std_logic; -- clock
INIT : in std_logic; -- initialize watchdog
KICK : in std_logic; -- restart timer
INTERVAL : in unsigned(31 downto 0); -- timer interval in clocks
TIMEOUT : out std_logic; -- timeout indicator
);
end watchdog_timer;
architecture behavioral of watchdog_timer is
process(CLK)
variable elapsed : std_logic; -- timeout register
variable counter : unsigned(31 downto 0); -- remaining clocks until timeout
begin
if rising_edge(CLK) then -- upon rising clock edge
if INIT = '1' then -- if watchdog is being initialized
counter <= INTERVAL; -- start timer
elapsed <= '0'; -- reset timeout indicator
elsif counter = 0 then -- else if watchdog interval has elapsed
elapsed <= '1'; -- indicate timeout; timer is halted
elsif KICK = '1' then -- else if watchdog is being kicked
counter <= INTERVAL; -- restart timer
else -- else
counter <= counter - 1; -- advance timer
end if;
end if;
TIMEOUT <= elapsed; -- send register output to TIMEOUT
end process;
end behavioral;

 Analog WDTs have a ''kick'' input and ''timeout'' output, but lack the clock input signal found in digital electronic watchdogs.
Circuitry and components vary widely among analog watchdogs, but in general, analog WDTs typically base their timing functions on
Analog WDTs have a ''kick'' input and ''timeout'' output, but lack the clock input signal found in digital electronic watchdogs.
Circuitry and components vary widely among analog watchdogs, but in general, analog WDTs typically base their timing functions on
 In the above example, if the application program fails to kick the watchdog (by restarting the PIT), the PIT will reach the end of the watchdog interval and generate an interrupt request (IRQ). The associated interrupt service routine (ISR) will then execute and take corrective action via programmed I/O, system calls, or other software-controlled operations.
In the above example, if the application program fails to kick the watchdog (by restarting the PIT), the PIT will reach the end of the watchdog interval and generate an interrupt request (IRQ). The associated interrupt service routine (ISR) will then execute and take corrective action via programmed I/O, system calls, or other software-controlled operations.
Arduino Watchdog Timer with Reset
- Article by Adityapratap Singh Embedded systems
 A watchdog timer (WDT, or simply a ''watchdog''), sometimes called a ''computer operating properly timer'' (''COP timer''), is an electronic or software
A watchdog timer (WDT, or simply a ''watchdog''), sometimes called a ''computer operating properly timer'' (''COP timer''), is an electronic or software timer
A timer or countdown timer is a type of clock that starts from a specified time duration and stops upon reaching 00:00. It can also usually be stopped manually before the whole duration has elapsed. An example of a simple timer is an hourglass ...
that is used to detect and recover from computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
malfunctions. Watchdog timers are widely used in computers to facilitate automatic correction of temporary hardware faults, and to prevent errant or malevolent software from disrupting system operation.
During normal operation, the computer regularly restarts the watchdog timer to prevent it from elapsing, or '' timing out''. If, due to a hardware fault or program error, the computer fails to restart the watchdog, the timer will elapse and generate a timeout signal. The timeout signal is used to initiate corrective actions. The corrective actions typically include placing the computer and associated hardware in a safe state and invoking a computer reboot
In computing, rebooting is the process by which a running computer system is restarted, either intentionally or unintentionally. Reboots can be either a cold reboot (alternatively known as a hard reboot) in which the power to the system is physi ...
.
Microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
s often include an integrated, on-chip watchdog. In other computers the watchdog may reside in a nearby chip that connects directly to the CPU, or it may be located on an external expansion card
In computing, an expansion card (also called an expansion board, adapter card, peripheral card or accessory card) is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot (also referred to as a bus sl ...
in the computer's chassis.
Applications
 Watchdog timers are commonly found in
Watchdog timers are commonly found in embedded system
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is e ...
s and other computer-controlled equipment where humans cannot easily access the equipment or would be unable to react to faults in a timely manner. In such systems, the computer cannot depend on a human to invoke a reboot if it hangs; it must be self-reliant. For example, remote embedded systems such as space probe
Uncrewed spacecraft or robotic spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input, such as remote control, or remote guidance. They may also be autonomous, in which th ...
s are not physically accessible to human operators; these could become permanently disabled if they were unable to autonomously recover from faults. In robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
s and other automated machines, a fault in the control computer could cause equipment damage or injuries before a human could react, even if the computer is easily accessed. A watchdog timer is usually employed in cases like these.
Watchdog timers are also used to monitor and limit software execution time on a normally functioning computer. For example, a watchdog timer may be used when running untrusted code in a sandbox
A sandbox is a sandpit, a wide, shallow playground construction to hold sand, often made of wood or plastic.
Sandbox or sand box may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Sandbox (band), a Canadian rock music group
* Sandbox (Gu ...
, to limit the CPU time available to the code and thus prevent some types of denial-of-service attack
In computing, a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyberattack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host co ...
s. In real-time operating system
A real-time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system (OS) for real-time computing applications that processes data and events that have critically defined time constraints. A RTOS is distinct from a time-sharing operating system, such as Unix ...
s, a watchdog timer may be used to monitor a time-critical task to ensure it completes within its maximum allotted time and, if it fails to do so, to terminate the task and report the failure.
Architecture and operation
Restarting
 The act of restarting a watchdog timer is commonly referred to as ''kicking'' the watchdog. In electronic watchdogs, kicking is typically done by writing to a watchdog control
The act of restarting a watchdog timer is commonly referred to as ''kicking'' the watchdog. In electronic watchdogs, kicking is typically done by writing to a watchdog control port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manch ...
or by setting a particular bit in a register
Register or registration may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Music
* Register (music), the relative "height" or range of a note, melody, part, instrument, etc.
* ''Register'', a 2017 album by Travis Miller
* Registration (organ), ...
. Alternatively, some tightly coupled watchdog timers are kicked by executing a special machine language
In computer programming, machine code is computer code consisting of machine language instructions, which are used to control a computer's central processing unit (CPU). For conventional binary computers, machine code is the binaryOn nonb ...
instruction. An example of this is the CLRWDT (clear watchdog timer) instruction found in the instruction set of some PIC microcontroller
PIC (usually pronounced as /pɪk/) is a family of microcontrollers made by Microchip Technology, derived from the PIC1640 originally developed by General Instrument's Microelectronics Division. The name PIC initially referred to ''Peripher ...
s.
In computers that are running operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s, electronic watchdog restarts are usually invoked through a device driver
In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabli ...
. For example, in the Linux operating system, a user space
A modern computer operating system usually uses virtual memory to provide separate address spaces or regions of a single address space, called user space and kernel space. This separation primarily provides memory protection and hardware prote ...
program will kick the watchdog by interacting with the watchdog device driver, typically by writing a zero character to or by calling a KEEPALIVE ioctl
In computing, ioctl (an abbreviation of input/output control) is a system call for device-specific input/output operations and other operations which cannot be expressed by regular file semantics. It takes a parameter specifying a request code; ...
. The device driver, which serves to abstract the watchdog hardware from user space programs, may also be used to configure the time-out period and start and stop the timer.
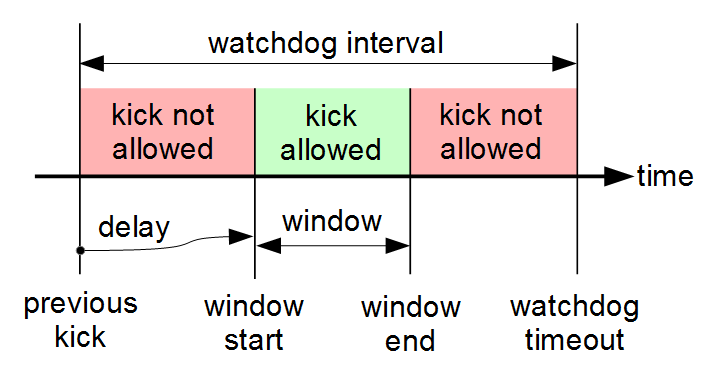
Some watchdog timers will only allow kicks during a specific time window. The window timing is usually relative to the previous kick or, if the watchdog has not yet been kicked, to the moment the watchdog was enabled. The window begins after a delay following the previous kick, and ends after a further delay. If the computer attempts to kick the watchdog before or after the window, the watchdog will not be restarted, and in some implementations this will be treated as a fault and trigger corrective action.
Enabling
A watchdog timer is said to be ''enabled'' when operating and ''disabled'' when idle. Upon power-up, a watchdog may be unconditionally enabled or it may be initially disabled and require an external signal to enable it. In the latter case, the enabling signal may be automatically generated by hardware or it may be generated under software control.Single-stage watchdog
Watchdog timers come in many configurations, and many allow their configurations to be altered. For example, the watchdog and CPU may share a commonclock signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and ...
as shown in the block diagram below, or they may have independent clock signals or in some cases the watchdog may have no clock signal at all. A basic watchdog timer has a single timer which, upon timeout, typically will reset the CPU:

Multistage watchdog
Two or more timers are sometimes cascaded to form a ''multistage watchdog timer'', where each timer is referred to as a ''timer stage'', or simply a ''stage''. For example, the block diagram below shows a three-stage watchdog. Depending on the design, this may be implemented with multiple timers, or by emulating multiple timers with a single timer and additional logic. In a multistage watchdog, only the first stage is kicked by the processor. Upon first stage timeout, a corrective action is initiated and the next stage in the cascade is started. As each subsequent stage times out, it triggers a corrective action and starts the next stage. Upon final stage timeout, a corrective action is initiated, but no other stage is started because the end of the cascade has been reached. Typically, single-stage watchdog timers are used to simply restart the computer, whereas multistage watchdog timers will sequentially trigger a series of corrective actions, with the final stage triggering a computer restart.
Time intervals
Watchdog timers may have either fixed or programmable time intervals. Some watchdog timers allow the time interval to be programmed by selecting from among a few selectable, discrete values. In others, the interval can be programmed to arbitrary values. Typically, watchdog time intervals range from ten milliseconds to a minute or more. In a multistage watchdog, each timer may have its own, unique time interval.Corrective actions
A watchdog timer may initiate any of several types of corrective action, including maskable interrupt,non-maskable interrupt
In computing, a non-maskable interrupt (NMI) is a hardware interrupt that standard interrupt-masking techniques in the system cannot ignore. It typically occurs to signal attention for non-recoverable hardware errors. Some NMIs may be masked, but ...
, hardware reset, fail-safe
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that, in the event of a failure causes, failure of the design feature, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. ...
state activation, power cycling
Power cycling is the act of turning a piece of equipment, usually a computer, off and then on again. Reasons for power cycling include having an electronic device reinitialize its set of configuration parameters or recover from an unresponsive stat ...
, or combinations of these. Depending on its architecture, the type of corrective action or actions that a watchdog can trigger may be fixed or programmable. Some computers (e.g., PC compatibles) require a pulsed signal to invoke a hardware reset. In such cases, the watchdog typically triggers a hardware reset by activating an internal or external pulse generator, which in turn creates the required reset pulses.
In embedded systems and control systems, watchdog timers are often used to activate fail-safe
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that, in the event of a failure causes, failure of the design feature, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. ...
circuitry. When activated, the fail-safe circuitry forces all control outputs to safe states (e.g., turns off motors, heaters, and high-voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
s) to prevent injuries and equipment damage while the fault persists. In a two-stage watchdog, the first timer is often used to activate fail-safe outputs and start the second timer stage; the second stage will reset the computer if the fault cannot be corrected before the timer elapses.
Watchdog timers are sometimes used to trigger the recording of system state information—which may be useful during fault recovery—or debug
In engineering, debugging is the process of finding the root cause, workarounds, and possible fixes for bugs.
For software, debugging tactics can involve interactive debugging, control flow analysis, log file analysis, monitoring at the ap ...
information (which may be useful for determining the cause of the fault) onto a persistent medium. In such cases, a second timer—which is started when the first timer elapses—is typically used to reset the computer later, after allowing sufficient time for data recording to complete. This allows time for the information to be saved, but ensures that the computer will be reset even if the recording process fails.
 For example, the above diagram shows a likely configuration for a two-stage watchdog timer. During normal operation the computer regularly kicks Stage1 to prevent a timeout. If the computer fails to kick Stage1 (e.g., due to a hardware fault or programming error), Stage1 will eventually timeout. This event will start the Stage2 timer and, simultaneously, notify the computer (by means of a non-maskable interrupt) that a reset is imminent. Until Stage2 times out, the computer may attempt to record state information, debug information, or both. As a last resort, the computer will be reset upon Stage2 timeout.
For example, the above diagram shows a likely configuration for a two-stage watchdog timer. During normal operation the computer regularly kicks Stage1 to prevent a timeout. If the computer fails to kick Stage1 (e.g., due to a hardware fault or programming error), Stage1 will eventually timeout. This event will start the Stage2 timer and, simultaneously, notify the computer (by means of a non-maskable interrupt) that a reset is imminent. Until Stage2 times out, the computer may attempt to record state information, debug information, or both. As a last resort, the computer will be reset upon Stage2 timeout.
Fault detection
A watchdog timer provides automatic detection of catastrophic malfunctions that prevent the computer from kicking it. However, computers can have other, less-severe types of faults which do not interfere with kicking, but which still require watchdog oversight. To support these, a computer system is typically designed so that its watchdog timer will be kicked only if the computer deems the system functional. The computer determines whether the system is functional by conducting one or more fault detection tests and will kick the watchdog only if all tests have passed. In computers that are running an operating system and multiple processes, a single, simple test might be insufficient to guarantee normal operation, as it could fail to detect a subtle fault condition and consequently kick the watchdog even though a fault condition exists. For example, in the case of the Linux operating system, a user-space watchdog
In computers that are running an operating system and multiple processes, a single, simple test might be insufficient to guarantee normal operation, as it could fail to detect a subtle fault condition and consequently kick the watchdog even though a fault condition exists. For example, in the case of the Linux operating system, a user-space watchdog daemon
A demon is a malevolent supernatural being, evil spirit or fiend in religion, occultism, literature, fiction, mythology and folklore.
Demon, daemon or dæmon may also refer to:
Entertainment Fictional entities
* Daemon (G.I. Joe), a character ...
may simply kick the watchdog periodically without performing any tests. As long as the daemon runs normally, the system will be protected against serious system crashes such as a kernel panic
A kernel panic (sometimes abbreviated as KP) is a safety measure taken by an operating system's Kernel (operating system), kernel upon detecting an internal Fatal system error, fatal error in which either it is unable to safely recover or con ...
. To detect less severe faults, the daemon can perform tests that cover various aspects of the system condition, including resource availability (e.g., memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembe ...
, file handles, CPU time), evidence of expected process activity (e.g., system daemons running, specific files being present or updated), overheating, and network activity.
Upon discovery of a failed test, the computer may attempt to perform a sequence of corrective actions under software control, culminating with a software-initiated reboot. If the software fails to invoke a reboot, the hardware watchdog timer — if available — will timeout and invoke a hardware reset. In effect, this is a multistage watchdog timer in which the software comprises the first and the hardware WDT the final stage. In a Linux system, for example, the watchdog daemon can be configured to attempt to perform a software-initiated reboot, which may be preferable to a hardware reset as it allows file systems to be safely unmounted and fault information to be logged prior to the reboot. It is essential, however, to have the insurance provided by a hardware WDT, to allow for the case in which a fault causes the daemon itself to malfunction, and thus become unable to invoke a reboot.
Implementation
Watchdog timers are implemented in various ways. Some electronic WDTs (e.g., Analog Devices MAX6324) use linear timing circuits that operate without a digital clock signal. Other electronic WDTs, and software WDTs, typically employ digital counters as timers and rely on a clock signal for proper operation.Electronic watchdogs
Electronic WDTs are usually implemented either as a stand-aloneintegrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
(IC) or as part of a more complex IC. Some stand-alone implementations contain only a WDT, whereas others bundle a WDT with other functions (e.g. supply voltage supervisors) in a common IC.
Many microcontrollers have a watchdog "module" consisting of a digital WDT and mechanisms for controlling and monitoring the WDT. Such modules typically include related control and status registers, circuitry for qualifying restart triggers ("kicks"), and routing control logic for the timeout signal. Some microcontrollers provide an analog WDT in lieu of a digital WDT. For example, Texas Instruments' TMS470 microcontroller has an analog WDT that employs an external capacitor and resistor to program the watchdog interval.
Digital watchdogs
In microcontrollers and other complex digital ICs, a digital WDT is typically instantiated by synthesizing it from a description written inVHDL
VHDL (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Program, VHSIC Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that can model the behavior and structure of Digital electronics, digital systems at multiple levels of abstraction, ran ...
, Verilog
Verilog, standardized as IEEE 1364, is a hardware description language (HDL) used to model electronic systems. It is most commonly used in the design and verification of digital circuits, with the highest level of abstraction being at the re ...
or some other hardware description language
In computer engineering, a hardware description language (HDL) is a specialized computer language used to describe the structure and behavior of electronic circuits, usually to design application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and to progra ...
. For example, the following VHDL code describes a simple WDT:
Analog watchdogs
capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
charging rates. For example, in the analog watchdog circuit shown to the right, electric current ''i'' gradually charges capacitor ''C'', causing voltage ''VC'' to ramp up (rise at a constant rate). In normal operation, periodic "kick" pulses are applied to the kick input. Each kick causes capacitor ''C'' to discharge, thus restarting the voltage ramp-up. However, if the kicks cease or become spaced too far apart in time, ''VC'' will rise above threshold voltage ''VTH'' and, as a result, the voltage comparator will assert the ''timeout'' signal.
Software watchdogs
Some software watchdog timers are implemented as standard software modules. Examples of these include "Softdog", a virtual device driver which emulates an electronic WDT and conforms to theLinux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
watchdog API, and MathWorks
The MathWorks, Inc. is an American privately held corporation that specializes in mathematical computing software. Its major products include MATLAB and Simulink, which support data analysis and simulation.
History
MATLAB was created in the 1 ...
' Software Watchdog Timer, a retriggerable one-shot timer which can be instantiated by dragging its GUI representation onto a block diagram. Other software WDTs are typically custom-designed to meet specific requirements.
Every software WDT depends on a timing reference to allow it to accurately track the passage of time. Various mechanisms are commonly available for this purpose. Depending on the computer, and if used, the operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
(OS), such mechanisms may include programmable interval timers, kernel timers, the system clock
In computer science and computer programming, system time represents a computer system's notion of the passage of time. In this sense, ''time'' also includes the passing of days on the calendar.
System time is measured by a ''system clock'', w ...
, and synchronization objects (e.g., semaphores) that support timed waits.
The design of a software WDT can be influenced by a number of factors, including the length of the watchdog interval, the time references available for WDT use, CPU loading, how soon the WDT must be kicked after relevant conditions have been met, whether the computer is running an OS and, if so, whether the WDT is intended to run in user or kernel mode. For example, in bare metal applications (program running without an OS), timing references are often limited to programmable interval timer
In computing and in embedded systems, a programmable interval timer (PIT) is a counter that generates an output signal when it reaches a programmed count. The output signal may trigger an interrupt.
Common features
PITs may be one-shot or periodi ...
s (PIT). In such cases, the WDT might be implemented with a PIT in a fashion similar to the flowchart
A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents a workflow or process. A flowchart can also be defined as a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step approach to solving a task.
The flowchart shows the steps as boxes of v ...
shown below:
See also
* Command-loss timer * Safe mode (spacecraft) * Deadman timer * Power-up timer * Heartbeat (computing) *Keepalive
A keepalive (KA) is a message sent by one device to another to check that the link between the two is operating, or to prevent the link from being broken.
Description
Once a TCP connection has been established, that connection is defined to be ...
Notes
References
External links
{{Wikibooks , Embedded Systems , Watchdog TimerArduino Watchdog Timer with Reset
- Article by Adityapratap Singh Embedded systems